3DS Server
Overview
To make 3DS 2.0 authentication transactions, it's necessary to integrate with a 3DS Server application, as the one provided by Software Express. This application communicates with the brand and the issuer to authenticate the cardholder, reducing fraud occurrences and allowing payments with debit cards.
The 3DS 2.0 protocol differs from it's 1.0 version in the possibility of having a frictionless authentication, which is a process that doesn't require additional interactions from the customer.
This documentation is focused on the interactions with the 3DS Server. For further information about the other components of the flow, refer to the EMVCo official documents.
Communication
To make a Web Service transaction, the whole communication must be done via HTTPS/TLS. It's important that the merchant's server supports encryption of a minimum of 128 bits. The merchant's server must make calls on specific addresses to do REST transactions.
Each service must be called using the base URL concatenated with the desired resource (see the chapter related to the service to be consumed). The HTTP method (GET, POST or PUT) indicates the expected action on the selected resource. Listed below are the 3DS Server base URLs:
Production base URL:
https://3ds.softwareexpress.com.br/
Homologation base URL:
https://mpi-homolog.softwareexpress.com.br/3ds-server/
Every call received by the services will be responded synchronously.
Attention:
Never use the IP instead of the 3ds.softwareexpress.com.br domain. The IP can change at any time without previous warning, so it's important to use the domain when accessing 3DS Server.
Important:
Besides the response parameters of the services described in this specification, 3DS Server can return other parameters without previous warning.
It's important that the application is prepared to receive the unknown parameters besides the fields already specified and simply ignore them.
Flows
The 3DS 2.0 protocol has 3 main flows:
- Frictionless: the whole authentication is performed without requiring additional interactions from the customer.
- Challenge: the information collected by the issuer are not enough to authenticate the cardholder. Thus, the customer must provide more data, directly on the issuer's site.
- Decoupled: the authentication is performed outside the 3DS protocol.
Glossary:
- 3DS Requestor: merchant or gateway (like e-SiTef)
- DS: Directory Server; represents the brand
- ACS: Access Control Server; represents the issuer
- AReq: Authentication Request, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
- ARes: Authentication Response, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
- CReq: Challenge Request, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
- CRes: Challenge Response, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
- RReq: Results Request, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
- RRes: Results Response, as described on the 3DS 2.0 protocol
Frictionless Flow
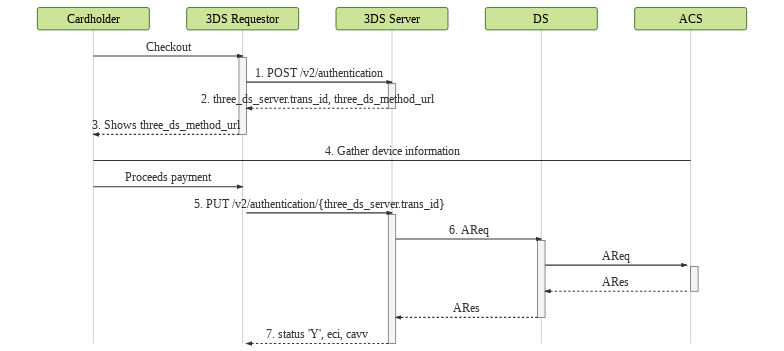
- 3DS Requestor creates the authentication transaction on 3DS Server, passing the customer's card number and its brand ID.
- 3DS Server validates whether the received card can be authenticated by the indicated brand. If positive, returns the 3DS Server transaction ID (
three_ds_server.trans_id) and the 3DS Method URL (three_ds_method_url) corresponding to the card. - The 3DS Method URL must be displayed on the customer's browser in an "invisible" 1 pixel frame.
- This will allow ACS to gather cardholder's device information directly.
- 3DS Requestor sends information for performing the authentication.
- 3DS Server generates an AReq and sends it to DS, which will then propagate it to ACS. The authentication result is returned to 3DS Server as content from ARes.
- If the authentication is successful, the following information will be returned: status (
three_ds_server.statusfield) with valueY, ECI (ecifield) and CAVV (authentication.valuefield), which must then be sent to the acquirer.
Challenge Flow
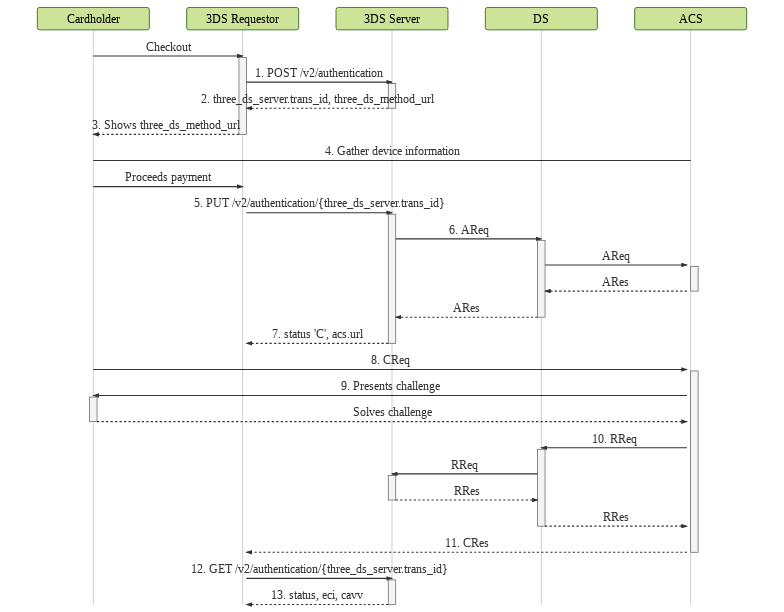
The steps 1 through 6 are the same as in the frictionless flow.
- The following information will be returned: status (
three_ds_server.statusfield) with valueCand the challenge URL (acs.urlfield). - 3DS Requestor prepares the CReq to be submitted from the customer's browser to the challenge URL.
- ACS displays its challenge screen so that the cardholder provides more information. Note that multiple interactions may be necessary to conclude this process.
- ACS sends RReq to DS, which will then propagate it to 3DS Server. This call is a notification informing the authentication result.
- ACS sends CRes to 3DS Requestor in its URL informed in step 5 (
notification_urlfield). This object contains the 3DS Server transaction ID. - 3DS Requestor queries the 3DS Server transaction to obtain the authentication result.
- 3DS Server returns the transaction information.
Flow Decoupled

The steps 1 through 6 are the same as in the frictionless flow.
- The status (
three_ds_server.statusfield) will be returned with valueD. - ACS will conduct its own authentication process, outside the 3DS 2.0 protocol.
- ACS sends RReq to DS, which will then propagate it to 3DS Server, informing the authentication result.
- 3DS Server informs the result to 3DS Requestor through its notification URL informed in step 5 (
decoupled_notification_urlfield). - 3DS Requestor responds to the notification with HTTP code 200.